Ancient Romans and Greeks used a plant called Silphium as a super effective contraceptive. But here’s the crazy part: they used it so much that it actually went extinct. Can you imagine that? This plant was so important to them, and they relied on it so heavily, that they ended up losing it forever.
Its heart-shaped seeds are thought to be the reason we associate the symbol with romance to this day.
It was cherished by the Romans and held such a special place in their hearts that they immortalized it in poems, songs, and esteemed works of literature. Its popularity was so profound that it contributed to the wealth and prosperity of the city of Cyrene, located in modern-day Shahhat, Libya, making it the wealthiest city in Africa.
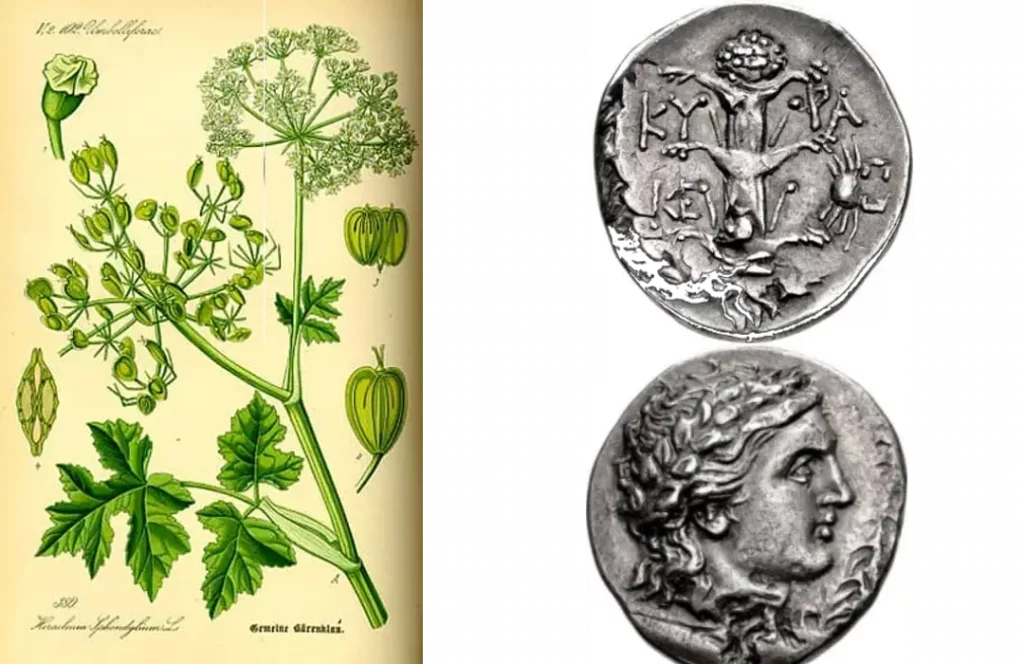

The history of silphium can be traced back to ancient times. It was first mentioned in writings by the Greek poet Hesiod in the 8th century BCE, and it was also referenced in the works of other ancient Greek writers, including Theophrastus and Aristotle. The ancient Greeks believed that silphium was a gift from the gods and valued it highly for its medicinal properties.
The Greek residents of Cyrene valued silphium to such an extent that they depicted its silhouette on their currency before relinquishing control to the Romans. The significance of this extraordinary plant was even recognized by Julius Caesar, who stored an impressive stockpile of 1,500 pounds (680 kilograms) in the official treasury.
It grew abundantly in the wild in ancient North Africa, particularly in the region that is now modern-day Libya. It had large heart-shaped leaves, tall stalks, and yellow flowers, which grew in clusters. It was unique in its flavor and aroma. The leaves and stems were used to flavor food and wine, while its juice was used as a natural remedy for a variety of ailments.
Not only as a contraceptive and in beverages, but Silphium was also used for treating a variety of medical conditions such as coughs, sore throats, and indigestion.
The plant grew only in a small region around Cyrene, which made it a rare and valuable commodity. As the plant became more and more scarce, its price skyrocketed, making it became more valuable and further increasing the demand for it. Despite efforts to cultivate the plant and protect it from overharvesting, it ultimately proved to be unsustainable and went extinct.

The loss of the Silphium plant had significant consequences for the ancient Greeks and Romans. Without access to this effective form of birth control, the population of these societies may have grown at a faster rate, leading to increased competition for resources and potentially putting strain on their economies and environments.
But the story of Silphium doesn’t end there. In fact, its extinction may have had even wider-reaching consequences. The plant was not only used as a contraceptive but also as a remedy for a variety of ailments. Its loss meant that people were no longer able to rely on it for these medical purposes, and they had to find alternative treatments. This had a major impact on the health and well-being of the ancient Greek and Roman people.
The extinction of the Silphium plant serves as a cautionary tale about the dangers of overconsumption and the need to carefully manage our use of natural resources. It also serves as a reminder of the important role that plants like Silphium have played in human history, and the need to preserve and protect the biodiversity of our planet. So the next time you hear about a plant or animal going extinct, remember the story of Silphium and the lessons it holds for us all.
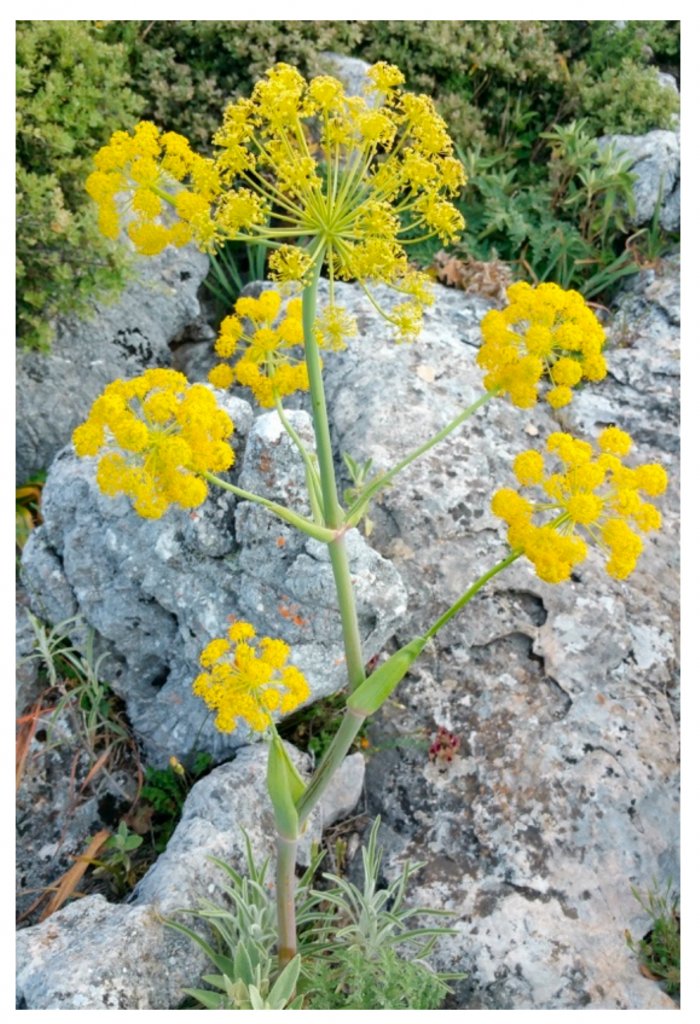

Today, the exact identity of silphium remains a mystery, as no specimens of the plant have survived. However, it is believed to have been related to the fennel or giant fennel plant, and its medicinal properties are thought to have been due to a resinous substance contained within the plant. The legacy of silphium can still be seen in ancient artwork and writings, which depict the plant and its many uses.
